Weighted Interval Scheduling
Problem1
Instead of just fitting as many tasks like regular interval scheduling problem, we have weight associates with the interval. Now we want to maximize the value.
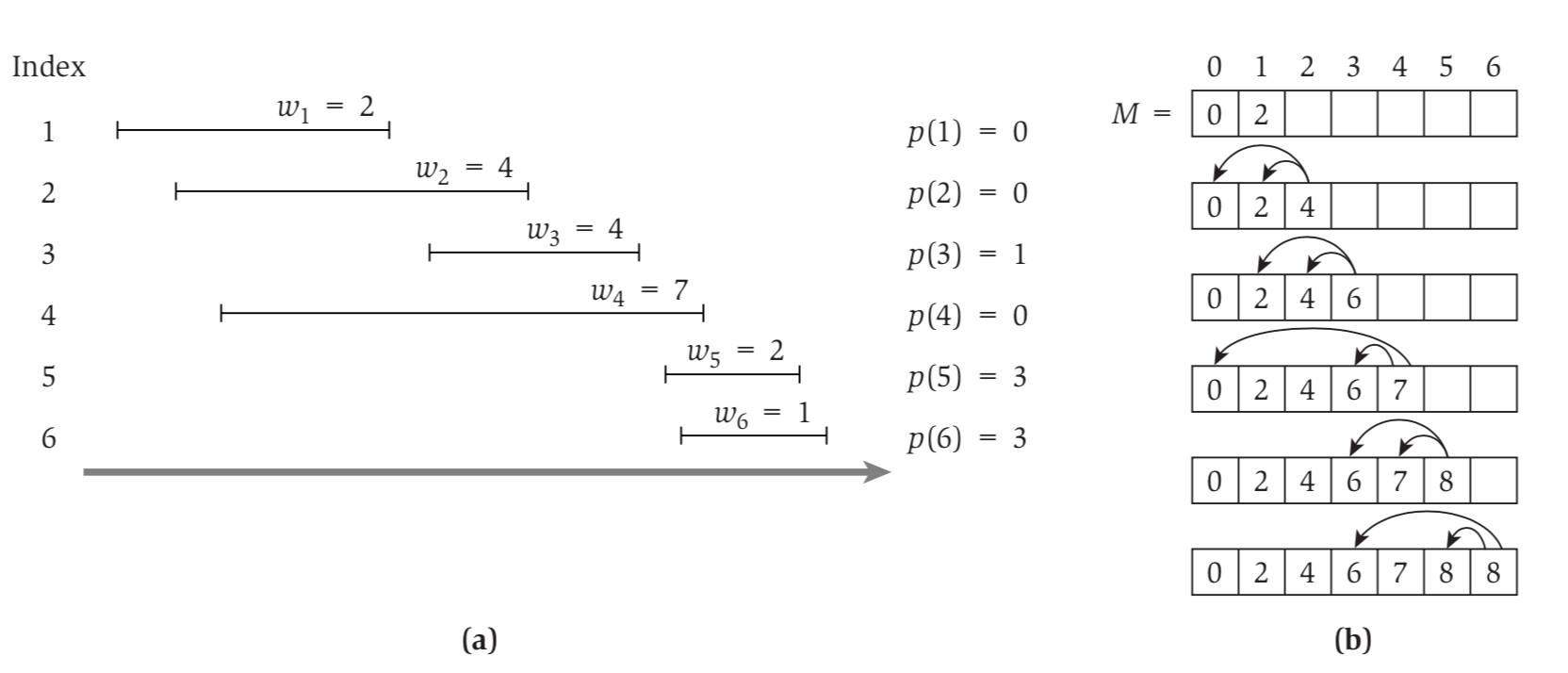
So basically, $f_i$ finish time sorted in non-decreasing order, $v_i$ is the value, and $s_i$ is the start time. We want $S \subseteq {1… n}$.
We also define $p(j)$ which is the largest i < j which is disjoint(compatible) with j.
Algorithm
Idea:
- Optimal O
- $n \in O$, find optimal for {1, p(n)}
- $n \notin O$, find optimal {1, n-1}.
- Let $O_j$ = optimal for {1, j}, $OPT(j) = value(O_j)$
- For above two cases then
- $OPT(j) = v_j + OPT(p(j))$
- $OPT(j) = OPT(j − 1)$
- $OPT(j) = max(v_j + OPT(p(j)), OPT(j − 1))$
Calculate the OPT
- Compute-Opt(j)
- If j=0 then
- Return 0
- Else
- Return max($v_j$+Compute-Opt(p(j)), Compute-Opt(j − 1)) Endif
- If j=0 then
However, the total numbers will be exponential.
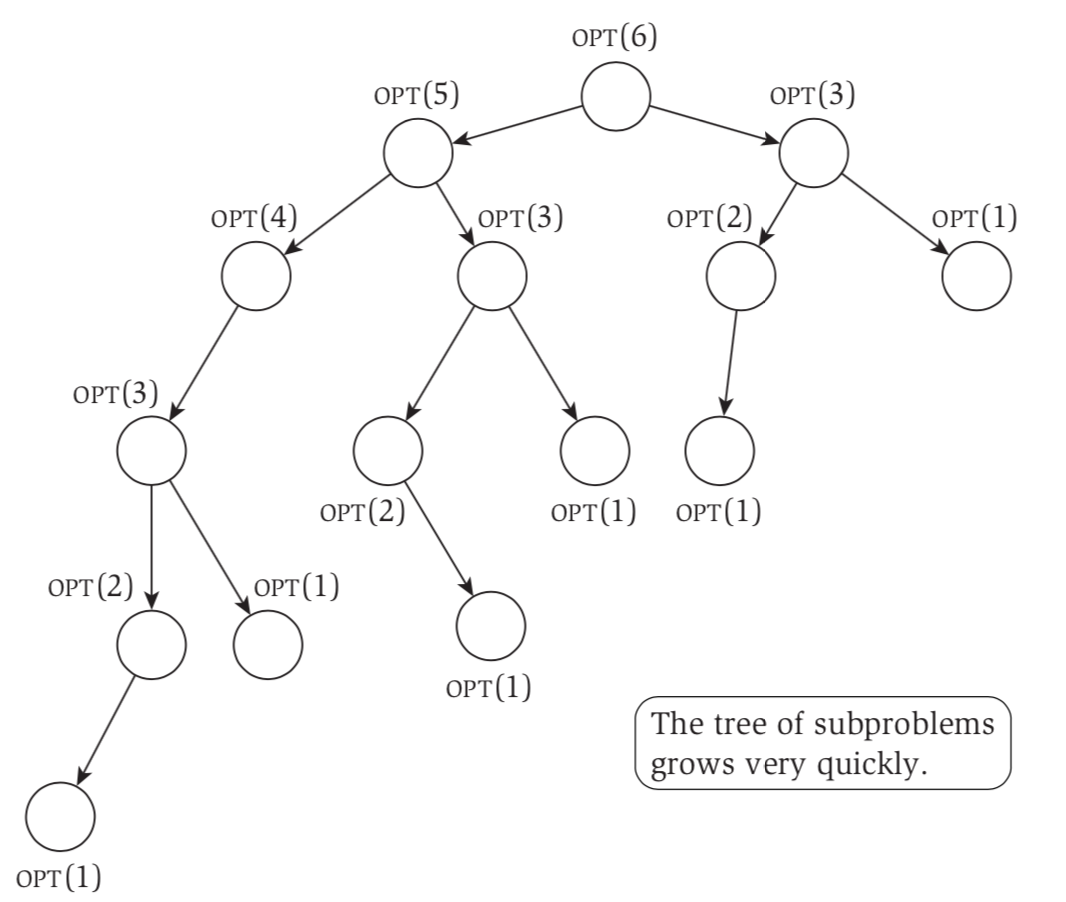
We memoize the intermediate step.
- M-Compute-Opt(j)
- If j=0 then
- Return 0
- Else if M[j] is not empty
- then Return M[j]
- Else
- Define M[j] = max($v_j$+M-Compute-Opt(p(j)), M-Compute-Opt(j − 1))
- Return M[j]
- Endif
- If j=0 then
Retrive Solution
- Find-Solution(j)
- If j=0 then
- Output nothing
- Else
- If $v_j$+M[p(j)] $\geq$ M[j−1] then
- Output j together with the result of Find-Solution(p(j))
- Else
- Output the result of Find-Solution(j − 1)
- Endif
- If $v_j$+M[p(j)] $\geq$ M[j−1] then
- Endif
- If j=0 then
Iterative Approach
- Iterative-Compute-Opt
- M[0]=0
- For j=1,2,…,n
- M[j]= max($v_j$ + M[p(j)], M[j − 1])
- Endfor
Analysis
In M-Compute-Opt M has at most n + 1 entries, the run time is O(n).
Find-solution will exceute at most n recursive call, so O(n).
- Algorithm Design by Jon Kleinber, Eva Tardos [return]