Counting Inversion
Problem
Application in ranking, also called corraborative filtering.
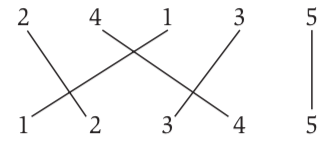
Comparing two rankings and decide how similar they are, or how many pairs are out of order.
To quantify this, we count the number of inversions. The inversion is defined as two indices i < j that $a_i > a_j$.
Algorithm
Brute-Force
$T(n) = O(n^2)$
Modified Merge-Sort
By leverage the merge process form merger-sort, we can count the number of inversion.
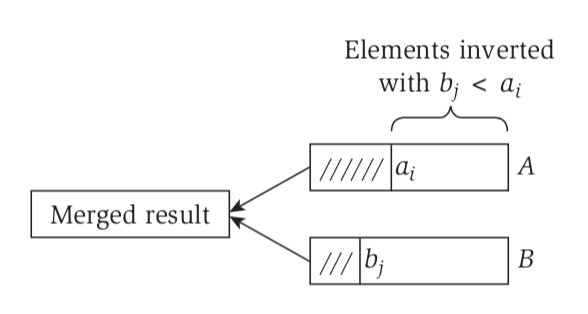
Basically, when the element from A is appended, there is not inversion. When we append element from B, the reamining number in the A is the number of inversion.
Merge and Count

Sort and Count
